概览
Android命令和IOS命令对照关系
| Android命令 | iOS命令 | |
|---|---|---|
| 安装应用 | adb install -r |
真机安装:fruitstrap -b UCWEB.app/XXX.ipa 模拟器安装:xcrun simctl install booted <XXX.app/XXX.ipa> ideviceinstaller -i |
| 卸载应用 | adb uninstall -k |
crun simctl erase [device ID] ideviceinstaller -u |
| 查看设备 | adb devices | instruments -s devices xcrun simctl list |
| 打开进程 | am start | open |
| 端口转发 | adb forward | tcprelay.py |
Android/iOS逆向&调试难度对比
| Android | iOS | |
|---|---|---|
| 逆向 | 编译出的可执行文件可能有dex/so和普通可执行文件。通过分析可以容易的知道哪个模块文件的功能 | Apple上架应用不允许动态加载模块(此处为动态下载然后加载),因此整个工程编译出来就是整个一个大binary。由于所有功能都混杂在一起,进行逆向分析的工程量较大,需要依靠Frida进行动态分析 |
| 脱壳 | Android上dex壳和so壳比较成熟,都是第三方平台开发的加壳工具。脱壳还原需要解除反调试等保护 | iOS上,Apple负责签名及加壳,因此脱壳方式简单且固定。iOS上唯一可以阻止脱壳的就是反注入标记,但是开启了这个标记会损失使用swift的能力,因此很多商业软件都没有加反注入 |
| 混淆 | Android分为Java代码和C++代码: * Java层混淆在商业软件中很常见 * C++关键代码采用OLLVM加密,分析耗时 |
iOS分为Objective-C代码和C++代码: * Objective-C代码混淆相对较少,易于使用Frida动态破解 * C++关键代码采用OLLVM加密,和Android难度等同 |
| 环境检测 | * 脱壳/重打包以后可以用过签名校验 文件MD5等方式检测出 * Android模拟器有很多,也很容易检测 |
* iOS上脱壳后有时候可以直接运行,因为加壳是苹果进行的操作,App不会通过MD5检验可执行文件本身,但是有可能会检测重打包(比如百度钱包的安全SDK),但是一般不会直接结束进程 * iOS不存在arm模拟器,因此不存在模拟器检测 |
| 调试 | Java:Android Studio/JDB/Frida C++:IDA Pro/GDB/Frida | C++/Objective-C/Swift:IDA Pro 7.0/LLDB/Frida |
| 反调试 | 存在Java层和C层调试的检测;可以多进程相互保护 | 存在C层调试检测,检测方式有限;单进程保护 |
| Root检测 | 存在 | 检测方法较多,没法完全屏蔽 |
Mac/iOS环境配置
Mac环境配置
安装brew
/usr/bin/ruby -e "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/master/install)"
安装wget
brew install binutils
brew install wget
brew install python
安装pip
wget https://bootstrap.pypa.io/get-pip.py
sudo su
python get-pip.py
pip install -U pip
安装应用
pip install frida
brew install gcc
brew install llvm
brew install automake
brew install cmake
brew install git
brew install gdbre
https://sourceware.org/gdb/wiki/BuildingOnDarwin
codesign -s gdb-cert /usr/local/bin/gdb
iOS环境配置
安装CYDIA工具:
OpenSSH 基本命令
Tcpdump
AppSync 绕过系统验证,随意安装ipa
Apple File Conduit 安装后可在手机助手显示系统目录
samba windows 文件共享
syslog 日志存放在/var/log/syslog
安装python pip
Ncdu du command
Lsof lsof command
File file command
Less less command
Cyscript
Apt struct 提供apt-get
Adv-cmds finger fingerd lsvfs last md ps
File-cmds chflags compress ipcrm ipcs pax
Basic-cmds msg uudecode uuencode write
Shell-cmds killall mktemp renice time which
System-cmds iostat login passwd sync sysctl
Diskdev-cmds mount quota fsck fstyp fdisk tunefs
Network arp ifconfig netstat route traceroute
Syslog syslogon syslogoff /var/log/syslog
Wget
GNU Debugger ar nm objdump ranlib strip addr2line c++filt gdb objcopy objdump readelf
(compile your code with –mcpu=arm1176jzf-s)
CYDIA常用源:
http://apt.thebigboss.org
http://apt.saurik.com
http://apt.modmyi.com
http://repo666.ultrasn0wn.com
http://ctdua.zodttd.com
http://apt.weifeng.com
http://apt.feng.com
http://repo.feng.com
http://repo.xarold.com
http://julio.xarold.com
http://crak.cn/repo/
http://iphone.tgbus.com/cydia/
https://build.frida.re
分析工具
| Android | Mac | iOS | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 跟踪工具 | strace ltrace Introspy | dtruss dtrace | Frida Cycript Introspy |
| 文件操作 | adb push/pull | scp | |
| 日志 | logcat | idevicesyslog | /var/log/syslog |
| 调试工具 | gdb jdb IDA gkidbg | gdb IDA lldb | gdb IDA lldb gikdbg |
| Hook框架 | XPosed/Cydia Substrate | Cydia Substrate | |
| 静态分析 | IDA dex2jar Apktool jadx jeb jd-gui | IDA classdump iNalyzer Hopper | IDA classdump iNalyzer Hopper |
Class-Dump用法
Class-dump是mac上的命令行工具用于解析Objective-C类接口,class-dump-z修复了一些bug并使用c++重写从而在mac, linux, win平台上运行,不支持x64 iphone,因此如果要解析mac os x程序的类,要用原始class-dump,而解析iphone的类使用class-dump-z
-
class-dump
运行于mac的工具用于解析objectc 运行时信息,生成classes, categories protocols,和otool –ov的结果类似,以objectivec语法表示更可读 -
Class-dump-z
速度快,便携且兼容各系统,修正ivar偏移处理,结构体名可读性高,属性化,隐藏继承和代理方法,参数名可读,修正头文件生成等
若由于AppStore加密等原因无法直接用classdump导出类的情况下,可以用cycript脚本weak_classdump在运行时进行同等操作
IDA反汇编
寻找oc函数调用栈
对于OC语法由于是通过消息机制进行函数调用的,因此无法直接找到调用者,这里通过脚本解决
import idc
def addxref(x, y, z):
"""
add reference for objc_meth_addr <=> objc_methname_addr <=> msgsend_call_addr
:param x: msgsend_call_addr
:param y: objc_meth_addr
:param z: objc_methname_addr
:return: nothing
"""
AddCodeXref(x, y, XREF_USER | fl_F)
## AddCodeXref(y, x, XREF_USER | fl_F)
## AddCodeXref(x, z, XREF_USER | fl_F)
## AddCodeXref(z, x, XREF_USER | fl_F)
AddCodeXref(y, z, XREF_USER | fl_F)
## AddCodeXref(z, y, XREF_USER | fl_F)
def addobjcref():
"""
add reference for math-o file
:return: nothing
"""
objc_meth_map = {}
methnamebegin = 0
methnameend = 0
forbitmeth = [
"alloc",
"allocWithZone:",
"allowsWeakReference",
"autorelease",
"class",
"conformsToProtocol:",
"copy",
"copyWithZone:",
"dealloc",
"debugDescription",
"description",
"doesNotRecognizeSelector:",
"finalize",
"forwardingTargetForSelector:",
"forwardInvocation:",
"hash",
"init",
"initialize",
"instanceMethodForSelector:"
"instanceMethodSignatureForSelector:",
"instancesRespondToSelector:",
"isEqual",
"isKindOfClass:",
"isMemberOfClass:",
"isProxy",
"isSubclassOfClass:",
"load",
"methodForSelector:",
"methodSignatureForSelector:",
"mutableCopy",
"mutableCopyWithZone:",
"performSelector:",
"performSelector:withObject:",
"performSelector:withObject:withObject:",
"respondsToSelector:",
"release",
"resolveClassMethod:",
"resolveInstanceMethod:",
"retain",
"retainCount",
"retainWeakReference",
"superclass",
"zone",
".cxx_construct",
".cxx_destruct",
]
# find the segment which contains objc method names
curseg = FirstSeg()
while curseg != 0xffffffff:
if "__objc_methname" == SegName(curseg):
methnamebegin = SegStart(curseg)
methnameend = SegEnd(curseg)
break
curseg = NextSeg(curseg)
# get objc method names
if methnamebegin != 0:
while methnamebegin < methnameend:
funcname = GetString(methnamebegin)
objc_meth_map[funcname] = methnamebegin
methnamebegin = methnamebegin + len(funcname) + 1
# get objc func table
funcmap = {}
addr = PrevFunction(-1)
while addr != 0xffffffff:
curname = GetFunctionName(addr)
if -1 != curname.find('['):
curname = curname.replace("[", "").replace("]", "")
curname = curname.split(" ")[1]
# may be more than one function with same sel but differenct class
if curname not in funcmap:
funcmap[curname] = []
funcmap[curname].append(addr)
addr = PrevFunction(addr)
# make xref
for (k, v) in objc_meth_map.items():
# find corresponding func addr
if k in funcmap and k not in forbitmeth:
farr = funcmap[k]
# find xref to code and make xref for each
curref = DfirstB(v)
while curref != 0xffffffff:
for f in farr:
addxref(curref, f, v)
curref = DnextB(v, curref)
print "added xref for " + k
if __name__ == "__main__":
addobjcref()
正常显示unicode中文字符
由于ida使用python对中文支持不好,这里通过脚本解决一定程度的问题
def find_utf16_string(addr):
start = SegStart(addr)
end = SegEnd(addr)
addr = start
while addr < end:
# get length
len = 1
while Name(addr + len) == "":
len = len + 1
totalstr = ""
for i in range(0, len, 2):
if Word(addr + i) > 0x100:
# read an unicode char
bytes = GetString(addr + i, 2)
try: # some chinese character not supported by python
comm = bytes.decode("utf-16")
if type(comm) == unicode:
comm = comm.encode("gbk")
else:
comm = '?'
except Exception as e:
comm = '?'
else:
# extract as ascii
comm = chr(Word(addr + i))
totalstr = totalstr + comm
MakeComm(addr, totalstr)
addr = addr + len
tofind = ["__ustring"]
seg = FirstSeg()
while seg != 0xffffffff:
if SegName(seg) in tofind:
find_utf16_string(seg)
seg = NextSeg(seg)
Debug for mac&ios
lldb调试
- 安装lldb和usb调试环境
brew install lldb libplist libusb usbmuxd ldid
wget http://cgit.sukimashita.com/usbmuxd.git/snapshot/usbmuxd-1.0.8.tar.bz2
tar xjfv usbmuxd-1.0.8.tar.bz2
cd usbmuxd-1.0.8/python-client/
python tcprelay.py -t 22:22 留作iphone命令行操作
python tcprelay.py –t 23946:23946 留作iphone调试
- 签名debugserver使之可以附加
-
- 创建签名文件entitlements.plist
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE plist PUBLIC "-//Apple//DTD PLIST 1.0//EN" "http://www.apple.com/DTDs/PropertyList-1.0.dtd">
<plist version="1.0">
<dict>
<key>com.apple.springboard.debugapplications</key>
<true/>
<key>get-task-allow</key>
<true/>
<key>task_for_pid-allow</key>
<true/>
<key>run-unsigned-code</key>
<true/>
</dict>
</plist>
-
- 签名完成后送入终端
codesign -s - --entitlements entitlements.plist -f debugserver
scp debugserver root@127.0.0.1:/bin/
上述过程在Xcode经历一次调试后自动完成,debugserver位于iOS /Developer/usr/bin
- 拷贝ARMDisassembler,提升代码可读性
/Applications/Xcode.app/Contents/Developer/Platforms/iPhoneOS.platform/DeviceSupport/?.?/DeveloperDiskImage.dmg的/Library/PrivateFrameworks/ARMDisassembler.framework
scp –r –p ARMDisassembler.framework root@127.0.0.1:/System/Library/PrivateFrameworks
- 启动lldb-server
./bin/debugserver
debugserver host:port [program-name program-arg1 program-arg2 ...] 启动调试
debugserver host:port --attach=<pid> 进程id附加调试
debugserver host:port --attach=<process_name> 进程名附加调试
- 启动lldb-client
lldb -> process connect connect://127.0.0.1:23946
IDA调试
由于lldb扩展了RSP协议(gdb remote serial debug protocol), Ida调试使用原始gdb调试协议,功能没有lldb和gikdbg强,对于app只能下断点跟踪,功能十分有限,目前还在研究协议转换中。由于默认编译的程序会有PIE标志,导致模块地址随机化,ida无法直接附加,因此使用010Editor删除PIE标志,上传到远程机器后chmod 777改为可执行即可。步骤如下:
- 使用010editor等工具将可执行文件去除pie标志(mach_header的flags MH_PIE=0x200000,注意选择正确的架构)
- 拷贝可执行文件并载入到ida:scp root@127.0.01:/path/to/file /path/to/file
- 启动server端:debugserver –x backboard *:1234 /path/to/file (或附加调试)
- 转发端口:python tcprelay.py –t 1234:1234
- 根据程序架构选择ida(x86 x64)设置ida为gdb调试,设置入口断点,设置调试地址和端口为127.0.0.1:1234,即可
Gikdbg调试
官网http://www.gikir.com/product.php,由ollydbg进一步开发的面向android和ios的汇编语言调试工具,支持静态分析elf/mach-o文件和动态调试android/iOS App,目前只支持arm系统,该软件运行在window上,适合调试dylib和可执行文件和简单的app
- 1.配置服务器
从官网下载gikdbg
scp $(GIKDBG)/iserver/gikir_iserver.deb root@127.0.0.1:/var/tmp
ssh root@127.0.0.1
dpkg -i /var/tmp/gikir_iserver.deb
重启后打开gikir_server app(清除占用6080端口的进程)
另一种安装方式是添加cydia源http://apt.feng.com/geekneo,安装gikir_iserver
- 2.启动客户端
执行Gikdbg.exe
iDebug/Login(USB)登录
iDebug/File/Attach附加调试 Open启动调试
目前gikdbg可以调试控制台、动态库、app程序,支持usb/wifi,支持注入动态库,首次调试的程序需要打补丁:
- 1) 删除MH_PIE标志,让进程每次加载基址固定;
- 2) 记录App的UUID值;
- 3) 如果是FAT格式的App则禁用最低以及最高的架构版本;
- 4) 如果是加密的App则解密该App;
- 5) 注入调试辅助动态库gikir_iserver_injecter.dylib;
Trace/Hook for mac/ios
系统支持
mac&ios进程加载器dyld提供了设置环境变量DYLD_INSERT_LIBRARIES 的方式向目标进程注入动态库,另外mac&ios系统支持的hook为在mach-o的__DATA __interpose节数据,源码如下,编译成mac和ios的binary即可,该法适用于普通程序,不适用于app,因为app无法用命令行直接启动
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
typedef struct interpose_s{
void* new_func;
void* orig_func;
} interpose_t;
int my_open(const char*, int ,mode_t);
__attribute__((used))
const interpose_t interposers[] __attribute__ ((section("__DATA, __interpose"))) =
{
{(void*)my_open, (void*)open},
};
int my_open(const char* path, int flags, mode_t mode)
{
int ret = open(path, flags, mode);
printf("%d = open %s\n",ret, path);
return ret;
}
void init() __attribute__((constructor));
void init()
{
printf("im in\n");
}
//gcc -dynamiclib l.c -o 1.dylib -Wall // compile to dylib
// lichao26de-iPhone:/tmp root# DYLD_INSERT_LIBRARIES=interpose.dylib cat 1
//im in
//3 = open 1
OC支持
load重写使该类在第一次加载时交换swizzled_setHidden和setHidden函数指针,导致调用swizzled_setHidden实际调用的是setHidden,反之亦然
##import <objc/runtime.h>
@implementation UIView(Loghiding)
- (BOOL)swizzled_setHidden {
NSLog(@"We're calling setHidden now!");
BOOL result = [self swizzled_setHidden];
return result;
}
+ (void)load {
Method original_setHidden;
Method swizzled_setHidden;
original_setHidden = class_getInstanceMethod(self, @selector(setHidden));
swizzled_setHidden = class_getInstanceMethod(self, @selector(swizzled_setHidden));
method_exchangeImplementations(original_setHidden, swizzled_setHidden);
}
@end
Frida
著名的跨平台注入&跟踪工具,普通安装方式pip install frida,越狱ios上安装方式:
- 添加源http://build.frida.re,安装frida,确保27042 27043端口不被占用
- 启动frida-server ./usr/sbin/frida-server
- 转发端口 python tcprelay.py –t 27042:27042 27043:27043
Cycript
著名的注入&跟踪工具,支持iOS/Mac/Android,支持ObjC/JavaScript1.7/C++11语法
远程连接Cycript
hcy=dlopen(”libcycript.dylib”,1) (可以使用各种方式将libcycript.dylib加载到进程中)
CYListenServer=(typedef void(short))(dlsym(hcy,”CYListenServer”))
CYListenServer(111) 调用函数
tcprelay –t 111:111 host上转发端口
cycript –r 127.0.0.1:111 host上连接server
编译JS
echo "[x*x for each(x in [1,2,3])]" | cycript -c > x.js
cat x.js
(function($cyv,x){$cyv=[];(function($cys){$cys=[1,2,3];for(x in $cys){x=$cys[x];$cyv.push(x*x)}})();return $cyv})()
?命令
?bypass 忽略错误
?debug 调试输出开关
?lower
?exit
?reparse 显示换行等字符
?syntax 语法高亮
?gc 强制js垃圾回收
语法特点
| JS type | ObjC type |
|---|---|
| number | NSNumber (CFNumber) |
| boolean | NSNumber (CFBoolean) |
| string | NSString |
| Array | NSArray |
| object | NSDictionary |
[[NSArray arrayWithObjects:
[NSNumber numberWithInt:41],
"foo",
[NSNumber numberWithBool:YES],
[NSArray arrayWithObjects:[NSNumber numberWithInt:8], [NSNumber numberWithInt:6], nil],
[NSDictionary dictionaryWithObjectsAndKeys:
[NSNumber numberWithInt:12], "a",
[NSNumber numberWithInt:46], "b",
nil],
[NSNumber numberWithInt:36],
nil] indexOfObject:"foo"]
可以直接简写为:[[41,"foo",true,[8,6],{a:12,b:46},36] indexOfObject:"foo"]
兼容OC语法
[obj msg:var]
@selector(selname)
obj->ivar
*ptr 打印结构体或类成员
objc->[key] 获取实例的某成员
&var 获取Objc实例地址
@class classname : superclass {} 定义Objc类
+ methodname {function body}
- methodname {function body}
@end
new classname
@”str” 等价于”str”
[super …]
Selector(selname) 声明selector
Functor(function body, type encoding) 定义ObjC函数
new Functor(function(x,y){return (x+y).toString(16);}, "*dd") (double, double) → char*
block = ^ int (int value) { return value + 5; } 声明block
基本功能
-
导入js模块
import "/tmp/test.js" -
导入cy模块
@import com.saurik.substrate.MS(对应/usr/lib/cycript0.9/com/saurik/substrate/MS.cy) -
导入nodejs/cy模块
util=require(“util”)
utils=require(“/tmp/utils.cy”)
-
返回上一次执行结果
_ -
获取可执行程序参数
system.args -
指针类型转换
Pointer(address, type encoding) 函数地址转换为encoding指定类型
Instance(address) 对象地址转换为ObjC对象地址
pt=(typedef int*)(oldpt) 强制类型转换
- 定义结构体
CGRect=(typedef struct {int x;int y;})
rect = new (struct CGRect)
rect.size 获取结构体大小
-
定义数组
arr=new (typedef char[10]) -
获取对象类型
obj.class
OC运行时功能
-
获取所有类
ObjectiveC.classes -
获取所有接口
ObjectiveC.protocols -
获取某实例所有方法
[MYCLASS (tab-key)] -
获取实例的所有变量
*obj -
由内存地址获取对象
[#0x18b6c8d0 show] -
获取所有类实例
choose(SBIconView) -
获取成员函数类型描述
selector.type(class)
selector(copyWithZone:).type(NSString) => @12@0:4^{_NSZone=}8.
- 修改函数
var oldm = NSObject.prototype.description
NSObject.prototype.description = function() { return oldm.call(this) + ' (of doom)'; }
[new NSObject init]
##"<NSObject: 0x100d11520> (of doom)"
调试功能
- 获取加载模块
utils.get_dyld_info()
ObjectiveC.images
-
修改内存权限
utils.mprotect(addr, size, utils.constants.PROT_READ) -
读写内存
var foo = new int
*foo = 0x12345678
utils.hexdump(foo, 4)
- 获取当前回溯栈
function bt(){
return [NSThread callStackSymbols];
}
-
执行命令
utils.getOutputFromTask(“/bin/ls”, []) -
调用函数
[obj msg: var] 调用oc函数
fopen(“/tmp”,”r”) 调用c函数
utils.apply("printf", ["%s %.3s, %d -> %c, float: %f\n", "foo", "barrrr", 97, 97, 1.5]) 反射调用c函数
- 反汇编
var method = class_getInstanceMethod(NSNumber,@selector(intValue));
var imp = method_getImplementation(method);
utils.disasm(imp, 10)
0x7fff83363b8c 1 55 push rbp
0x7fff83363b8d 3 4889e5 mov rbp, rsp
0x7fff83363b90 2 4157 push r15
0x7fff83363b92 2 4156 push r14
0x7fff83363b94 2 4155 push r13
- 汇编
var n = [NSNumber numberWithLongLong:10]
var method = class_getInstanceMethod([n class], @selector(longLongValue));
var imp = method_getImplementation(method);
utils.asm(imp, 'mov eax, 42; ret;')
Hook功能
- 记录OC函数调用(需要substrate)
utils.logify(NSNumber, @selector(numberWithDouble:))
[NSNumber numberWithDouble:1.5] //触发logifyt
2014-07-28 02:26:39.805 cycript[71213:507] +[<NSNumber: 0x10032d0c4> numberWithDouble:1.5]
注意:对静态成员函数,第一参为object_getClass(类名);对普通成员函数,第一参为object_getClass(实例) 底层实现:
cy# @import com.saurik.substrate.MS
cy# var oldm = {};
cy# MS.hookMessage(NSObject, @selector(description), function() {
return oldm->call(this) + " (of doom)";
}, oldm)
cy# [new NSObject init]
##"<NSObject: 0x100203d10> (of doom)"
- 记录C函数调用(需要substrate)
utils.logifyFunc("fopen", 2)
apply("fopen", ["/etc/passwd", "r"]); //触发logifyt
2015-01-14 07:01:08.009 cycript[55326:2042054] fopen(0x10040d4cc, 0x10040d55c)
cy# @import com.saurik.substrate.MS
cy# extern "C" void *fopen(char *, char *);
cy# var oldf = {}
cy# var log = []
cy# MS.hookFunction(fopen, function(path, mode) {
var file = (*oldf)(path, mode);
log.push([path.toString(), mode.toString(), file]);
return file;
}, oldf)
cy# fopen("/etc/passwd", "r");
(typedef void*)(0x7fff774ff2a0)
cy# log
[["/etc/passwd","r",(typedef void*)(0x7fff774ff2a0)]]
其他功能
-
获取所有控件元素
utils.find_subviews() -
获取所有viewcontroller
utils.find_subview_controllers() -
获取cpu类型
utils.getCpuType() -
获取坐标
manager=choose(CLLocationManager)[0]
[manager location]
- 获取bundleid
NSBundle.mainBunble.bundleIdentifier
其他CYCRIPT模块
- cycript-utils https://github.com/Tyilo/cycript-utils/blob/master/utils.cy
- weak-dump 运行时的class-dump
- classdump-dyld weak-dump升级版,支持x64 ``
iOS实例分析
-
方式一:MachO格式注入
在mach-o格式中增加LOAD_DYLIB command节,添加dylib,重签名即可 -
方式二:调试器(LLDB/GDB/Cycript等)注入
LLDB/GDB:po dlopen("/usr/lib/test.dylib",1)
Cycript:dlopen("/usr/lib/test.dylib",1) 调试状态下也可使用cycript
- 方式三:MobileLoader注入 CydiaSubstrate的MobileLoader组件用于加载第三方dylib给指定程序,MobileLoader首先在启动时使用DYLD_INSERT_LIBRARIES加载自身,之后加载/Library/MobileSubstrate/DynamicLibraries下的所有动态库,由于是全局的默认会在所有程序中加载,可以采用过滤配置plist文件加载dylib(iOS9以后必须存在plist才准予加载),plist文件名与dylib名相同:
- Bundle:必须匹配app(s)的bundle-id才准予加载
- Classes:必须在目标进程中实现指定类(s)才准予加载
- Executables:必须匹配可执行文件名才准予加载
Filter = {
Executables = (“mediaserverd”);
Bundles = (“com.apple.sprintboard”, “net.whatsapp.WhatsApp”);
Mode = “Any”
};
- 方式一:Cydia Hook框架
MSImageRef MSMapImage(const char* file) 加载dylib
cont void* MSImageAddress(MSImageRef image)
bool MSHookProcess(pid_t pid, const char* library) 远程线程方式(vm_)注入dylib
MSImageRef MSGetImageByName(const char* file) 获取模块基址,优于dlopen
Void* MSFindSymbol(MSImageRef image, const char* name) 获取函数地址,优于dlsym
char* MSFindAddress(MSImageRef image, void** address)
Void MSHookFunction(void* symbol, void* replace, void** result) hook c函数
IMP MSHookMessage(Class _class, SEL sel, IMP imp, const char* prefix) hook oc消息
Void MSHookMessageEx(Class _class, SEL sel, IMP imp, IMP* result) hook oc消息
void MSHookClassPair(Class target, Class hook, Class old) 封装MSHookMessageEx
Hook c函数底层实现仍然是arm汇编的inline hook
Hook oc函数底层实现则是利用objective-c runtime function
对于 rettype funcname(type1 param1, type2 param2)的函数:
hook c function 方式1 -- MSHookFunction:
rettype (*old_funcname)(type1 param1, type2 param2);
rettype new_funcname(type1 param1, type2 param2)
{
……….work before hook……….
old_funcname(param1, param2);
……….work after hook…………
}
MSHookFunction((void*) funcname, (void*)&new_funcname, (void**)&old_funcname);
hook c function 方式2 – MSHookFunction-MSHook-MSHack:
MSHook(rettype, funcname, type1 param1, type2 param2)
{
……….work before hook……….
_funcname(param1, param2);//注意前面加’_’
……….work after hook…………
}
MSHookFunction(funcname, MSHake(funcname))
hook oc function 方式1 - MSHookMessageEx
hook oc function 方式2 - MSHookClassPair
hook oc function 方式3 - MSHookInterface
- Theos越狱框架开发
优点:方便,一键部署,缺点:调试麻烦
$THEOS/bin/nic.pl
iphone/tweak
export THEOS_DEVICE_IP=???
make package install
- XCode开发
特点:和前者相反,调试方便,只需要如前述修改mach-o type为可执行程序即可调试
#include <CydiaSubstrate.h>
void* handle = dlopen(“libsubstrate.dylib”, 1);
typedef void (*HOOK)(void*, void*, void**);
HOOK MSHookFunction = (HOOK)dlsym(handle, “MSHookFunction”);
MSHookFunction((void*)funcname, (void*)&oldfunc, (void**)&newfunc);
- 方式二:frida/frida-trace frida安装:mac/linux/win下执行pip install frida,iOS上从frida源安装服务端,安好后服务端每次开机启动,占用端口27042/27043,因此在客户端执行python tcprelay.pt –t 27042:27042 27043:27043
frida-ps –R 枚举所有进程
frida-ps –R –a 枚举所有app进程
frida-ps –R –a –i 枚举所有安装的app及其bundle name
frida-trace –R –p PID 附加到进程(按进程id)
frida-trace –R –n name 附加到进程(按进程名,例如百度商户)
frida-trace –R –f FILE 拉起进程并跟踪(例如com.baidu.bshoppush)
hook c function frida-trace –i “recv*” –i “send*” ….
hook oc function frida-trace –m “-[NS* draw*]” …
实例:跟踪商户app二维码操作
frida-trace -R -f com.baidu.bshoppush -m "-[QRCode* *]" -f com.baidu.bshoppush
对生成的js进行编辑,自定义输出数据可以在控制台得到相应显示
获取JSPatch下发代码:
frida-trace –U –f com.baidu.waimai –m “+[JPEngine *evaluate*]”
js脚本内容
var data=new ObjC.Object(args[2]);
log(data.toString());
log(Thread.backtrace(this.context, Backtracer.ACCURATE).map(DebugSymbol.fromAddress).join("\n") + "\n");
Jailbreak Development Tools
Theos
$ $THEOS/bin/nic.pl
NIC 1.0 - New Instance Creator
------------------------------
[1.] iphone/application
[2.] iphone/library
[3.] iphone/preference_bundle
[4.] iphone/tool
[5.] iphone/tweak
Choose a Template (required): 1
Project Name (required): iPhoneDevWiki
Package Name [com.yourcompany.iphonedevwiki]: net.howett.iphonedevwiki
Authour/Maintainer Name [Dustin L. Howett]:
Instantiating iphone/application in iphonedevwiki/...
Done.
$
IOSOpenDev
用于XCode的越狱程序开发插件http://iphonedevwiki.net/index.php/IOSOpenDev
Mac&iOS file format analysis
otool 类似于objdump,可以解析objc类信息
class-dump objc类接口信息解析成可读objc头文件
OBJC_HELP 环境变量打日志
OBJC_HELP=1 ./build/Debug/HelloWorld
objc: OBJC_HELP: describe Objective-C runtime environment variables
objc: OBJC_PRINT_OPTIONS: list which options are set
objc: OBJC_PRINT_IMAGES: log image and library names as the runtime loads
them
NSObjCMessageLoggingEnabled 环境变量用于打印objc_msgSend调用日志
NSObjCMessageLoggingEnabled=Yes ./hello
Hello World!
-[dcbz@megatron:~/code/HelloWorld/build]$ cat /tmp/msgSends-6686
+ NSRecursiveLock NSObject initialize
+ NSRecursiveLock NSObject new
+ NSRecursiveLock NSObject alloc
....
+ Talker NSObject initialize
+ Talker NSObject alloc
+ Talker NSObject allocWithZone:
- Talker NSObject init
- Talker Talker say:
- Talker NSObject release
- Talker NSObject dealloc
machoview 查看格式的gui工具 https://github.com/gdbinit/MachOView.git
dtrace 跟踪mac上objective-c函数调用
分析iOS二进制文件的过程:
- 1.如果是app store下载的app,需要先用工具砸壳,将代码数据区内存解密
- 2.从手机将文件拷贝到主机使用ida分析
- 3.将砸壳生成的文件修改PIE标志并重新签名,替换原始app,方便动态分析
砸壳
由于class-dump等工具的流行,App Store上发布的软件都经过加密处理(LC_ENCRYPTION_INFO所标志的区域),加载器dyld对可执行文件校验,根据fat头选择合适的架构,处理所有的command,使用posix_spawn函数启动进程。ios上所有第三方代码都需要使用developer id代码签名,而代码签名作为数据存储在mach-o格式command结构中,因此fat格式中得每个架构的文件都分别签名,并由内核验证,如果验证失败则会收到停止信号而退出。在越狱机上可以通过ldid进行伪签名通过签名校验。进行了加密后,无法直接用ida查看内部结构
-
dumpencrypted
https://github.com/stefanesser/dumpdecrypted/blob/master/dumpdecrypted.c,该工具注入目标进程内存,利用解密后的内存转储数据得到脱壳文件,时机在dyld加载后,init(__mod_init_func)节加载前 -
clutch
https://github.com/KJCracks/Clutch/releases,命令行工具。该工具使用posix_spawn函数以暂停态(POSIX_SPAWN_START_SUSPENDED)和ASLR关闭模式创建目标程序子进程,从而使目标进程不执行任何代码而得到系统解密的内存,后使用task_for_pid从mach port得到目标进程内存,最后更新头部的LC_ENCRYPTION_COMMAND,合并成文件。
mach-o格式分析
相关数据结构定义在/Developer/SDKs/iPhoneOS.sdk/usr/include/mach-o/loader.h,总体结构包括:header结构、command表、数据区。header结构:用于指明cpu类型(x86?arm?…),文件类型(动态库?可执行文件?…),command表位置;如果文件中包含多个cpu的可执行文件,则会存在FAT header头指明每个cpu的文件位置,因此一个mach-o文件的开头可能是mach_header结构,此时文件只包含一种cpu架构的可执行文件,也可能是fat_header,存储不同mach_header的偏移
struct mach_header {
uint32_t magic; /* mach magic number identifier */
cpu_type_t cputype; /* cpu specifier */
cpu_subtype_t cpusubtype; /* machine specifier */
uint32_t filetype; //静态库.a 目标文件.o 动态库.dylib 可执行文件 ………….
uint32_t ncmds; /* number of load commands */
uint32_t sizeofcmds; /* the size of all the load commands */
uint32_t flags; /* flags */
};
command表相当于pe的节表,描述文件和内存进行映射的表,包括__PAGEZERO(标记可执行文件的第一个节)、__TEXT、__DATA、__OBJC(objective-c运行库表用于描述类信息)、__IMPORT、__LINKEDIT(符号、字符串、重定位表),常用的command如下:
LC_SEGMENT/LC_SEGMENT_64 描述文件中得节和内存映射关系
struct segment_command { /* for 32-bit architectures */
uint32_t cmd; /* LC_SEGMENT */
uint32_t cmdsize; /* includes sizeof section structs */
char segname[16]; /* segment name */
uint32_t vmaddr; /* memory address of this segment */
uint32_t vmsize; /* memory size of this segment */
uint32_t fileoff; /* file offset of this segment */
uint32_t filesize; /* amount to map from the file */
vm_prot_t maxprot; /* maximum VM protection */
vm_prot_t initprot; /* initial VM protection */
uint32_t nsects; /* number of sections in segment */
uint32_t flags; /* flags */
};
LC_LOAD_DYLIB 要加载的动态库
struct dylib {
union lc_str name; /* library's path name */
uint32_t timestamp; /* library's build time stamp */
uint32_t current_version; /* library's current version number */
uint32_t compatibility_version; /* library's compatibility vers number*/
};
struct dylib_command {
uint32_t cmd; /* LC_ID_DYLIB, LC_LOAD_{,WEAK_}DYLIB,
LC_REEXPORT_DYLIB */
uint32_t cmdsize; /* includes pathname string */
struct dylib dylib; /* the library identification */
};
LC_MAIN 描述入口点
struct entry_point_command {
uint32_t cmd; /* LC_MAIN only used in MH_EXECUTE filetypes */
uint32_t cmdsize; /* 24 */
uint64_t entryoff; /* file (__TEXT) offset of main() */
uint64_t stacksize;/* if not zero, initial stack size */
};
LC_LOAD_DYLINKER 描述mach-o可执行文件加载器
struct dylinker_command {
uint32_t cmd; /* LC_ID_DYLINKER, LC_LOAD_DYLINKER or
LC_DYLD_ENVIRONMENT */
uint32_t cmdsize; /* includes pathname string */
union lc_str name; /* dynamic linker's path name */
};
LC_CODE_SIGNATURE 用codesign和ldid(plist)签名生成的结构,用于突破沙盒等权限限制
struct linkedit_data_command {
uint32_t cmd; /* LC_CODE_SIGNATURE, LC_SEGMENT_SPLIT_INFO,
LC_FUNCTION_STARTS, LC_DATA_IN_CODE,
LC_DYLIB_CODE_SIGN_DRS or
LC_LINKER_OPTIMIZATION_HINT. */
uint32_t cmdsize; /* sizeof(struct linkedit_data_command) */
uint32_t dataoff; /* file offset of data in __LINKEDIT segment */
uint32_t datasize; /* file size of data in __LINKEDIT segment */
};
LC_ENCRYPTION_INFO/LC_ENCRYPTION_INFO_64 用于appstore加密程序
struct encryption_info_command {
uint32_t cmd; /* LC_ENCRYPTION_INFO */
uint32_t cmdsize; /* sizeof(struct encryption_info_command) */
uint32_t cryptoff; /* file offset of encrypted range */
uint32_t cryptsize; /* file size of encrypted range */
uint32_t cryptid; /* which enryption system,
0 means not-encrypted yet */
};
LC_SYMTAB 符号表
LC_UUID 文件唯一标识
App目录和文件
用户App位置/var/mobile/Applications/[GUID]/
- AppName.app 目录存放app静态数据和代码
- Documents目录存放持久化数据,和iTunes同步;包括sql数据库
- Library目录存放配置文件、缓存和cookie
- tmp目录存放临时文件
Objective C Reversing
研究方式:命令行编译+二进制对比+调试
Debug: clang/gcc –g -fobjc-arc -framework Foundation FKPerson.m main.m
Release: clang/gcc –O3 -fobjc-arc -framework Foundation FKPerson.m main.m
交叉编译arm: clang/gcc -x objective-c -arch armv7 -g -fobjc-arc -isysroot /Applications/Xcode.app/Contents/Developer/Platforms/iPhoneOS.platform/Developer/SDKs/iPhoneOS9.3.sdk -framework Foundation main.m (arch=i386 x86_64 armv7 arm64)
objective-c编译为c++源码:clang/gcc –rewrite-objc –framework Foundation main.m
- meta-class 每个类都存在元类,
- super-class 父类
- root-class 根类
- selector 选择器(存储为字符串,其内存位置与方法一一对应)
- imp 普通函数指针
- id 通用数据类型
杂项
字符串存储:
@”” => 实际编译为CFString结构
Class CFString : objc_object
{
longlong info;
char* data;//真正的字符串存储位置
longlong length;//字符串长度
}
synchronized锁:
@synchronized(expression1){
expression2;
}
实际编译生成为:
id lock = expression1
objc_sync_enter(lock)
expression2;
objc_sync_exit(lock)
选择器@selector:
@selector(x) => 实际编译为”x”
关键字@encode:
@encode(type) => 实际编译为 该类型的描述符
关键字@autorelease:
@autorelease{expression;} => 实际编译为
objc_autoreleasePoolPush(…)
expression;
objc_autoreleasePoolPop
快速枚举for:
for(type a in b) {expression;}=> 实际编译为
for(int i=0;i<b.selRef_countByEnumeratingWithState_objects_count_;i++){
expression;
}
nil值:=> (void*)0
Function
传参所用寄存器,适用于普通函数和成员函数(id,sel)
arm架构:
a1 R0
a2 R1
a3 R2
a4 R3
a5 [sp+0]
a6 [sp+4]
…. arm64架构:
a1 W0
a2 W1
a3 W2
a4 W3
a5 W4
a6 W5
a7 W6
a8 [sp+0]
a9 [sp+8]
a10 [sp+16]
a11 [sp+24]
…….
X86架构(默认调用约定):
a1 [esp+0]
a2 [esp+4]
a3 [esp+8]
a4 [esp+8]
a5 [esp+12]
a6 [esp+16]
…….
x86_64架构:
a1 rdi
a2 rsi
a3 rdx
a4 rcx
a5 r8
a6 r9
a7 [rsp+0]
a8 [rsp+8]
……
Block
用于定义匿名函数,等价于lambda表达式,形式如下:
^ [返回值类型] (类型1 形参1, 类型2 形参2, ...)
{
}
定义Block变量形式如下:
返回值类型 (^块变量名) (类型1, 类型2, ...);
int (^hypot)(int, int) = ^(int num1, int num2)
{
returnnum1 * num1 + num2 * num2;
};
NSLog(@"%d",hypot(3,4));
编译得到:
v3= ((int (__fastcall *)(_QWORD, _QWORD, _QWORD))*(&__block_literal_global8 +2))(&__block_literal_global8, 3LL, 4LL);
NSLog(&cfstr_D, (unsigned int)v3);
其中__block_literal_global8将函数等相关信息封装成类(这点和vs-win一致),___main_block_invoke_2正是函数体实现:
__const:0000000100001060 ___block_descriptor_tmp7dq 0 ; DATA XREF:__const:0000000100001098o
__const:0000000100001068 dq 20h
__const:0000000100001070 dq offset aI16@?0i8i12 ; "i16@?0i8i12"
__const:0000000100001078 align 20h
__const:0000000100001080___block_literal_global8 dq offset __NSConcreteGlobalBlock
__const:0000000100001080 ; DATAXREF: _main+87o
__const:0000000100001088 dq 50000000h
__const:0000000100001090 dq offset ___main_block_invoke_2
__const:0000000100001098 dq offset___block_descriptor_tmp7
从源码Block_private.h可以得到构造的Block结构体
struct Block_layout
{
void *isa;
volatile int32_t flags; // contains ref count
int32_t reserved;
void (*invoke)(void *, ...);//实际调用的函数
struct Block_descriptor_1 *descriptor;
// imported variables
};
struct Block_descriptor_1
{
uintptr_t reserved;
uintptr_t size;
};
struct Block_descriptor_2
{
void (*copy)(void *dst, const void *src);
void (*dispose)(const void *);
};
struct Block_descriptor_3
{
const char *signature;
const char *layout; //contents depend on BLOCK_HAS_EXTENDED_LAYOUT
};
从内部实现看,Block代码能生成3种类型:
NSGlobalBlock 代码中未操作外部变量或操作全局变量(如上例)
NSStackBlock 代码中操作外部栈变量
NSMallocBlock 代码中操作外部堆变量
下面分别讨论
第一种情况:
代码为最开始的例子,可见其中没有用到外部变量
实际产生的代码为:
int ___main_block_invoke(Block_layout this,int num1, int num2)
{
returnnum1 * num1 + num2 * num2;
}
Block_layout __block_literal_global =
{
__NSConcreteGlobalBlock,
0x50000000,
0,
&___main_block_invoke,
&___block_descriptor_tmp,
}
__block_literal_global. ___main_block_invoke(&__block_literal_global,3, 4);
第二种情况:
代码如下
__blockint my = argc;
int(^hypot)(int, int) = ^(int num1, int num2)
{
my+= 1;
returnnum1 * num1 + num2 * num2;
};
NSLog(@"%d%d", hypot(3, 4), my);
实际产生的代码为:
block_descriptor ___block_descriptor_tmp =
{
0,
28,
___copy_helper_block_,
___destroy_helper_block_,
"i16@?0i8i12",
16
};
int ___main_block_invoke(Block_layout this,int num1, int num2)
{
this->___stack_variable->my+= 1;
returnnum1 * num1 + num2 * num2;
}
Block_layout __block_literal_global =
{
__NSConcreteStackBlock,
0xC2000000,
0,
&___main_block_invoke,
&___block_descriptor_tmp,
&___stack_variable//存放所有栈变量
};
void __copy_helper_block_()
{
_Block_object_assign(my,argc)
}
void __destroy_helper_block_()
{
_Block_object_dispose(my,argc)
}
__block_literal_global.___block_descriptor_tmp.___copy_helper_block_();
__block_literal_global. ___main_block_invoke(&__block_literal_global,3, 4);
..................
__block_literal_global.___block_descriptor_tmp.___destroy_helper_block_();
第三种情况:
需要开启arc,暂无研究
Class
类型定义
Object描述通用对象,所有类继承自该类 struct objc_object{
Class isa; //描述类型
}
Class描述类,相当于模板,创建实例和使用静态方法时使用 struct objc2_class : objc2_object{//runtime/
//Class isa; //Class对象的Class即meta class
Class superclass; //父类Class
cache_t cache; //缓存调用过的成员函数
objc2_class_rw* data;
}
class_rw动态类数据,内存中呈现形式 struct objc2_class_rw{//runtime/objc-runtime-new.h class_rw_t
int flags; //标志位
int version;
objc2_class_ro* ro;
method_array_t methods; //链表结构方便随时添加函数
property_array_t properties
protocol_array_t protocols;
Class firstSubclass;
Class nextSiblingClass;
char* demangledName;
}
类属性flags
RW_REALIZING 0x80000 class has started realizing
RW_HAS_INSTANCE_SPECIFI
class_ro静态类数据,二进制文件中呈现形式,在初始化后设置REALIZE转化成新结构class_rw struct objc2_class_ro{//runtime/objc-runtime-new.h class_ro_t
int flags; //标志位
int instanceStart; //在Instance中第一个ivar偏移
int instanceSize; //Instance大小
int reserved;
byte* ivar_layout;
char* name; //对应类名
objc2_meth_list* base_meths; //类拥有的成员方法(静态成员在metaclass中)
objc2_prot_list* base_prots; //类遵守的接口
objc2_ivar_list* ivars; //类拥有的成员变量
byte* weak_ivar_layout;
objc2_prop_list* base_props; //使用@property定义的属性
}
类属性flags
RO_META 1 meta-class
RO_ROOT 2 root-class
RO_HAS_CXX_STRUCTORS 4 has .cxx_construct/destruct
RO_HAS_LOAD_METHOD 8 has +load
RO_HIDDEN 16 visibility=hidden
RO_EXCEPTION 32 has attribute(objc_exception)
RO_REUSE_ME 64 available for reassignment
RO_IS_ARR 128 class compiled with –fobjc-arc
RO_HAS_CXX_DTOR_ONLY 256 has .cxx_destruct but no .cxx_construct
RO_FROM_BUNDLE 0x20000000 class is in unloadable bundle
RO_FUTURE 0x40000000 class is unrealized future
RO_REALIZED 0x80000000 class is realized
Instance——实例结构,操作实例或类成员函数中使用 struct objc_instance : objc_object{
//Class isa;
Member1; //成员变量1,2,3….
Member2;
}
Method List——描述类结构中包含的成员函数 struct objc2_method_list{
int entrySize; //每个objc2_method结构大小
int count; //后接count个objc2_method
}
Method——描述单个成员函数 struct objc2_method {
SEL method_name //方法名 setName:andAge:
char *method_types //方法类型 v28@0:8@16i24
IMP method_imp //实际地址 ptr of setNameandAge
}
成员函数指针定义:typedef id (*IMP)(id, SEL, ...);
函数修饰符method_types runtime.h
‘b’-bitfield
‘B’-bool
‘c’-char
‘C’-uchar
‘d’-double
‘f’-float
‘i’-int
‘I’-uint
‘l’-long
‘L’-ulong
‘n’-in for input
‘N’-inout both for input and output
‘o’-out for ouput
‘O’-bycopy instead of using a proxy/NSDistantObject, pass or return a copy of the object
‘q’-longlong
‘Q’-ulonglong
‘r’-const constant
‘R’-byref use a proxy(default)
‘s’-short
‘S’-ushort
‘v’-void
‘V’-oneway 允许在不同线程和进程使用,不可阻塞调用线程直到返回
‘^’-pointers
‘@’-object
‘[‘-array begin
‘]’-array end
‘{‘-structure begin
‘}’-structure end
‘(‘-union begin
‘)’-union end
‘#’-class
‘:’-selector
‘*’-char pointer
‘%’-atom
‘!’-vector
‘?’-undefine
Structure: returntype—stacksize—[argumenttype—bitoffset]*
v28@0:8@16i24 -> void stacksize=28 (pointer, selector, pointer, int)
Ivar List struct objc2_ivar_list{
int entrySize; //每个objc2_ivar结构大小
int count; //后接count个objc2_ivar
}
Ivar struct objc2_ivar{
int* offset; //存储该变量相对Instance结构偏移
char* name; //变量名
char* type; //类型描述符
int alignment_raw; //对齐
int size; //变量占用空间
}
Protocol List——描述遵守的接口 struct objc2_protocol_list{
longlong count;//后接count个Protocol
}
Protocol——描述单个接口 struct objc2_protocol : objc_object{
//Class isa;
char* mangledName;
objc2_protocol_list* protocols
objc2_method_list* instanceMethods;
objc2_method_list* classMethods;
objc2_method_list* optionalInstanceMethods;
objc2_method_list* optionalClassMethods;
objc2_method_list* instanceProperties;
int size;
int flag;
char** extendedMethodTypes;
char* _demangledName;
}
Property List——描述使用@property关键字定义的成员变量(和普通成员变量分开存放) struct objc2_prop_list{
int entrySize; //每个objc2_prop结构大小
int count; //后接count个objc2_prop
}
Property——描述单个@property成员变量 struct objc2_prop{
char* name;
char* attributes;// T@"NSString",&,V_a1
}
返回普通类型的静态成员函数调用
[FKPerson foo] objc_msgSend([FKPerson class], “foo”)
void _cdecl foo(FKPerson* self, SEL selector)
返回普通类型的普通成员函数调用
[person say] objc_msgSend(person, “say”)
void _cdecl say(FKPerson * self, SEL selector)
返回普通类型的多参数成员函数调用
[person setName:@”1” andAge:500] objc_msgSend(person, “setName:andAge:”, @”1”, 500)
void _cdecl setName:andAge:(FKPerson* self, SEL selector, NSString* name, int age)
成员函数中调用父类函数,父函数返回普通类型
[super init] objc_msgSendSuper(make_super super, “init”)
返回栈结构体的成员函数调用
[person func] objc_msgSend_stret(person, “func”)
成员函数中调用父类函数,父函数返回栈结构体
[super func] objc_msgSendSuper_stret(self, “func”)
返回栈浮点数 arm:不使用objc_msgSend_fpret
i386:float|double|long double使用objc_msgSend_fpret
x86-64:long double使用objc_msgSend_fpret
成员函数分析
- 1.每增加一个成员函数,类模板会增加method,由于名称一一对应,同一个类不允许存在同名函数
- 2.每个成员函数前两个参数分别是实例指针self和选择器SEL,之后才是用户为其定义的参数
- 3.带(+)修饰的成员函数本质为静态成员,属于该类的meta-class类成员,因此位于meta-class函数表中,而普通成员函数位于该类的函数表中
- 4.和c++不同的是,成员函数调用方式和普通函数相同,因此可以通过反射替换成普通函数
成员变量分析
- 1.每增加一个成员变量,类模板Class会增加ivar,以后使用该类模板创建的实例的对象结构也会增加该元素
- 2.只要有一个实际使用的成员变量,就会产生”类名.cxx_destruct”析构函数
- 3.根据成员变量属性为weak/strong,在进行赋值操作时采用objc_storeWeak/objc_storeStrong,默认类型为strong
- 4.对public成员变量的操作语法采用myclass->field形式,产生的逻辑也和c结构体相同,而更常规的方式是将成员变量写成@property中,这样编译器会自动为成员变量生成相应的getter和setter函数,使用kvc(键值编码)时会自动调用(msgsend)这些函数
meta-class存在的原因
- 1.直接从类对象进行的操作,例如调用静态成员函数,并不属于某个实例,因此需要存在于类类型中
- 2.当自身被子类化(setsuperclass)时,父类并不等同于所属类(isa != superclass),同理构造一个类要提供其isa
Objc_msgSend调用流程
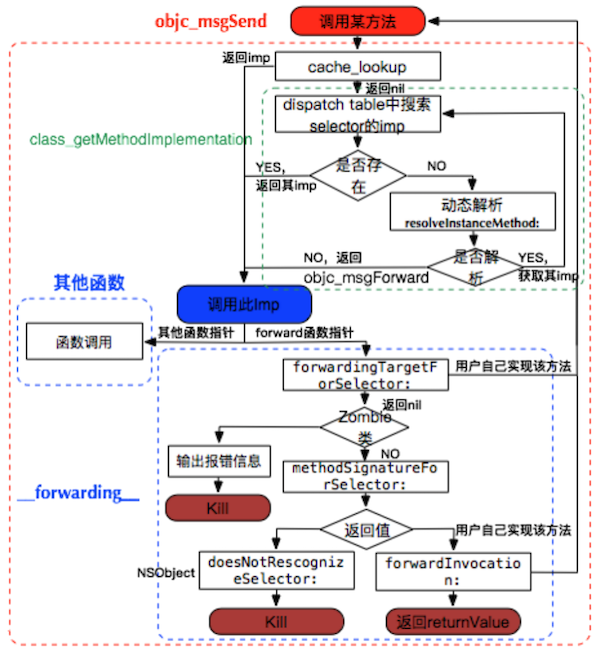
- 1.根据对象的isa找到类,在类的dispatch table中查找selector
- 2.如果未找到则找到该类的父类,并在父类的dispatch table中查找selector,直到NSObject类(该过程中优先查找cache)
- 3.如果所有子类和父类都无法找到该函数,则进行msgForward,如果用户添加了动态实现(resolveInstanceMethod)则调用
- 4.如果上一步失败,则尝试找到一个能响应该消息的对象(forwardingTargetForSelector),如果能找到则转发给他
- 5.如果上一步失败,则尝试获取一个方法签名(methodSignatureForSelector),如果获取不到直接抛异常
- 6.调用用户自己实现的forwardInvocation
Runtime Ability
Object id object_copy(id obj, size_t size) 拷贝实例内容
Class object_getClass(id obj) 返回Instance对应的Class
Class object_setClass(id obj, Class cls) 绑定Instance的Class
BOOL object_isClass(id obj) 判断所属
char* object_getClassName(id obj) 获取类名
void* object_getIvar(id obj, Ivar ivar) 获取成员变量值(按Ivar)
void object_setIval(id obj, Ivarl ivar, id value) 设置成员变量值
Ivar object_getInstanceVariable(id obj, char* name, void* value) 获取成员变量值(按变量名)
Ivar object_setInstanceVariable(id obj, char* name, void* value) 设置成员变量值
Class Class objc_getClass(char* name) 返回指定类名的(类型)对象
Class objc_getaMetaClass(char* name) 返回指定类名的meta-class对象
Class objc_lookUpClass(char* name) 返回指定类名且已注册的的(类型)对象
int objc_getClassList(Class* buffer, int bufferCount) 返回所有已注册类
Class* objc_copyClassList(int* outCount) 返回所有已注册类
char* class_getName(Class cls) 获取类名
BOOL class_isMetaClass(Class cls) 是否meta-class
Class class_getSuperClass(Class cls) 获取父类
Class class_setSuperClass(Class cls, Class newSuper)设置父类
int class_getVersion(Class cls) 获取版本
void class_setVersion(Class cls, int version) 设置版本
size_t class_getInstanceSize(Class cls) 获取实例大小
Ivar class_getInstanceVariable(Class cls, char*name) 获取实例Ivar
Ivar* class_copyIvarList(Class cls, int* outCount)
Method class_getInstanceMethod(Class cls, SEL name) 获取非静态方法
Method class_getClassMethod(Class cls, SEL name) 获取静态方法
IMP class_getMethodImplementation(Class cls, SEL name) 获取方法实现
BOOL class_conformsToProtocol(Class cls, Protocol* protocol)是否遵守协议
Method* class_copyMethodList(Class cls, int* outCount)
Protocol* class_copyProtocolList(Class cls, int* outCount)
objc_property_t class_getProperty(Class cls, char* name)
objc_property_t class_copyPropertyList(Class cls, int* outCount)
uchar* class_getIvarLayout(Class cls)
BOOL class_addMethod(Class cls, SEL name, IMP imp, char* types) 增加函数(绑定普通函数)
BOOL class_replaceMethod(Class cls, SEL name, IMP imp, char* types)替换函数
BOOL class_addIvar(Class cls, char* name, size_t size, uchar alignment, char* types)添加变量
BOOL class_addProtocol(Class cls, Protocol* protocol) 增加协议
BOOL class_addProperty(Class cls, char* name, objc_property_attribute_t* attrib,int count)
BOOL class_replaceProperty(Class cls, char* name, objc_property_attribute_t* attrib,int count)
void class_setIvarLayout(Class cls, uchar layout)
id class_createInstance(Class cls, size_t extrabytes) 创建实例
id objc_constructInstance(Class cls, void* bytes) 创建实例
void* objc_destructInstance(id obj)
Class objc_allocateClassPair(Class superclass, char* name, size_t extrabytes) 创建类和元类
void objc_registerClassPair(Class cls) 注册类
Class objc_duplicateClass(Class original, char* name, size_t extraBytes) 复制类
Method SEL method_getName(Method m) 获取函数名
int method_getNumberOfArguments
char* method_getTypeEncoding 获取函数类型字段
void method_getArgumentType 获取参数类型
void method_getReturnType 获取返回值类型
IMP method_getImplementation
IMP method_setImplementation(Method m, IMP imp)设置函数实现
void method_exchangeImplementations(Method m1, Method m2)
Ivar char* ivar_getName(Ivar v) 获取Ivar名
char* ivar_getTypeEncodeing(Ivar v) 获取Ivar类型字段
ptrdiff_t ivar_getOffset(Ivar v) 获取该ivar在instance中得偏移
Attribute ……
Protocol objc_copyProtocolList
protocol_getName
protocol_copyProtocolList
protocol_allocateProtocol
protocol_registerProtocol
protocol_addProtocol
protocol_addProperty
其他 char** objc_copyImageNames(int* outcount) 获取加载的动态库
char* class_getImageName(Class cls) 获取某类所属动态库
char** objc_copyClassNamesForImage(char* image, int* outCount)获取动态库中所有类
objc_loadWeak 获取weak值
objc_storeWeak 设置weak值
objc_setAssociatedObject 设置关联
objc_getAssociatedObject 获取关联
objc_removeAssociatedObjects 移除所有关联,恢复对象到原始状态
其他
arc类型转换:
普通指针和objc指针转换:(实现调试器中任意内存当作类操作)
id obj1 = [[class1 alloc] init];
void* p = (__bridge void*)obj1;
id obj2 = (__bridge id)p;
@property:
@property(?,?,…)用于快速生成类成员及getter setter,其修饰符如下:
atomic 原子操作,线程安全(默认)
objc_getProperty objc_setProperty_atomic
nonatomic 非线程安全 ‘N’
readwrite 具有setter getter(默认)
readonly 具有getter ‘R’
assign 简单赋值(默认)
copy setter方法中深度复制传入对象 ‘C’
objc_getProperty objc_setProperty_atomic_copy
retain setter方法中对传入对象引用计数加一 ‘&’
strong 强引用(默认),和retain相似 ‘&’
初始化/赋值= 销毁objc_storeStrong
weak 对象消失后指针置nil ‘W’
初始化objc_initWeak 赋值objc_loadWeakRetained 销毁objc_destroyWeak/objc_autoreleaseReturnValue
__unsafe_unretain 对象引用计数不加一,对象释放后不置nil
autorelease 对象加入自动释放池 对应objc_autorelease
异常处理
objc提供异常处理机制
@try{
expr1;
}
@catch(NSException* ex){
expr2;
}
@finally{
expr3;
}
产生的流程如下:
......
flag = 0
expr1
label1:
expr3
...
if(flag & 1)
objc_exception_rethrow()
return
tail:
if(..)
{
expr2;
}
goto label1;
@throw语句层产生:objc_exception_throw()
Reflection
Objective-C是一种反射型语言,可以在运行时获取和修改自身状态,其中的实现存在于libobjc.A.dylib库中,这些“运行时”能力源于objective-c类结构组织较为灵活,并提供了操作自身结构的接口,同时在生成的可执行文件(mach-o)中存在_OBJC节,这些节中提供了足够的类构成信息,而Mac端gdb可以解析这些结构,而正由于objc提供了如此多的信息,因此也比c++在同等情况下逆向难度低一些。
LC_SEGMENT.__OBJC.__cat_cls_meth
LC_SEGMENT.__OBJC.__cat_inst_meth
LC_SEGMENT.__OBJC.__string_object
LC_SEGMENT.__OBJC.__cstring_object
LC_SEGMENT.__OBJC.__message_refs
LC_SEGMENT.__OBJC.__sel_fixup
LC_SEGMENT.__OBJC.__cls_refs
LC_SEGMENT.__OBJC.__class
LC_SEGMENT.__OBJC.__meta_class
LC_SEGMENT.__OBJC.__cls_meth
LC_SEGMENT.__OBJC.__inst_meth
LC_SEGMENT.__OBJC.__protocol
LC_SEGMENT.__OBJC.__category
LC_SEGMENT.__OBJC.__class_vars
LC_SEGMENT.__OBJC.__instance_vars
LC_SEGMENT.__OBJC.__module_info
LC_SEGMENT.__OBJC.__symbols
java与objc反射对比
| objc | java | |
|---|---|---|
| 获取类 | NSClassFromString myClass.class [myClass class] | Class.forName myClass.class |
| 检查继承 | isKindOfClass isMemberOfClass conformsToProtocol | class.isAssignableFrom instanceOf class.isInstance |
| 获取函数 | @selector NSSelectorFromString | getMethod |
| 调用函数 | perfromSelector objc_msgSend | invoke |
iOS Attack&Defense
AntiDebug - AntiAntiDebug
- sysctl P_TRACED标志 检测调试 可以检测调试器和跟踪器,但是不能检测注入和cycript:
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/sysctl.h>
static int check_debugger( ) __attribute__((always_inline));
int check_debugger( )
{
size_t size = sizeof(struct kinfo_proc);
struct kinfo_proc info;
int ret,name[4];
memset(&info, 0, sizeof(struct kinfo_proc));
name[0] = CTL_KERN;
name[1] = KERN_PROC;
name[2] = KERN_PROC_PID;
name[3] = getpid();
if((ret = (sysctl(name, 4, &info, &size, NULL, 0)))){
return ret; //sysctl() failed for some reason
}
return (info.kp_proc.p_flag & P_TRACED) ? 1 : 0;
}
- ptrace PT_DENY_ATTACH 防止调试 可以阻止调试器附加:
##import <dlfcn.h>
##import <sys/types.h>
typedef int (*ptrace_ptr_t)(int _request, pid_t _pid, caddr_t _addr, int _data);
##if !defined(PT_DENY_ATTACH)
##define PT_DENY_ATTACH 31
##endif // !defined(PT_DENY_ATTACH)
void disable_gdb() {
void* handle = dlopen(0, RTLD_GLOBAL | RTLD_NOW);
ptrace_ptr_t ptrace_ptr = dlsym(handle, "ptrace");
ptrace_ptr(PT_DENY_ATTACH, 0, 0, 0);
dlclose(handle);
}
##ifdef __arm__
asm volatile(
“mov r0,#31\n”
“mov r1,#0\n”
“mov r2,#0\n”
“mov r12,#26\n”
“svc #80\n”
##endif
##ifdef __arm64__
asm volatile(
“mov x0,#26\n”
“mov x1,#31\n”
“mov x2,#0\n”
“mov x3,#0\n”
“mov x16,#0\n”
“svc #128\n”
##endif
直接附加调试器会产生segmentation fault:11 启动调试程序会在ptrace执行后退出 调试已经被调试的进程:直接失败产生日志:(os/kern) invalid task Exiting
- 反反调试:hook相应函数
##import <substrate.h>
##if !defined(PT_DENY_ATTACH)
##define PT_DENY_ATTACH 31
##endif
static int (*_ptraceHook)(int request, pid_t pid, caddr_t addr, int data);
static int $ptraceHook(int request, pid_t pid, caddr_t addr, int data) {
if (request == PT_DENY_ATTACH) {
request = -1;
}
return _ptraceHook(request,pid,addr,data);
}
%ctor {
MSHookFunction((void *)MSFindSymbol(NULL,"_ptrace"), (void *)$ptraceHook, (void **)&_ptraceHook);
}
- isatty检测调试 isatty函数在给定文件描述符被附加到调试器控制台时返回1,否则返回0
if(isatty(1)){
NSLog(@”Being Debugged isatty”);
}
else{
NSLog(@”isatty() bypassed”);
}
- task_get_exception_ports检测调试
调试器通常会监听异常端口,因此可以用task_get_exception_ports循环遍历以校验该端口是否设置
struct ios_execp_info{
exception_mask_t masks[EXC_TYPES_COUNT];
mach_port_ports[EXC_TYPES_COUNT];
exception_behavior_t behaviors[EXC_TYPES_COUNT];
thread_state_flavor_t flavors[EXC_TYPES_COUNT];
mach_msg_type_number_t count;
}
struct ios_execp_info* info = malloc(sizeof(struct ios_execp_info));
kern_return_t kr = task_get_exception_ports(mach_task_self(),EXC_MASK_ALL,info->masks,&info->count,info->ports
,info->behaviors,info->flavors);
for(int i=0;i<info->count;i++){
if(info->ports[i] != 0 || info->flavors[i] == THREAD_STATE_NONE){
NSLog(@”Beging debugged”);
}
else{
NSLog(@“bypassed”);
}
}
- _RESTRICT节——防注入
加载器dyld(ios7.0以后)源码中关于DYLD_环境变量的逻辑pruneEnvironmentVariables
switch (sRestrictedReason) {
case restrictedNot:
break;
case restrictedBySetGUid:
dyld::log("main executable (%s) is setuid or setgid\n", sExecPath);
break;
case restrictedBySegment:
dyld::log("main executable (%s) has __RESTRICT/__restrict section\n", sExecPath);
break;
case restrictedByEntitlements:
dyld::log("main executable (%s) is code signed with entitlements\n", sExecPath);
break;
}
3种情况下DYLD环境变量会被忽视
- 1.可执行文件设置了setuid setgid位
- 2.可执行文件有__restrict节
- 3.可执行文件有特殊代码签名
由于受app store的限制,1和3都不能实现,而2可以设置Other linker flags为-Wl,-sectcreate,__RESTRICT,__restrict,/dev/null 使用该方法可以禁止dylib的注入,在生成的mach-o文件中会多出一个__RESTRICT节 这种方式是可以防止启动注入和运行时注入的,尝试用dumpdecrypted脱壳时会产生类似如下的日志:
dyld: warning, LC_RPATH @executable_path/Frameworks in /var/mobile/Applications/[id]/?.app/* being ignored in restricted program because of @executable_path
尝试用cycript附加会产生如下输入:
dlopen(/usr/lib/libcript.lib, 5): Library not loaded: /System/Library/PrivateFrameworks/JavaScriptCore.framework/JavaScriptCore
referenced from: /usr/lib/libcript.dylib
reason: image not found
*** _assert(status == 0):../Inject.cpp(143):InjectLibrary
而使用lldb则可以正常附加调试
- anti-anti-debug
改restrict节名,重签名(ldid –S)即可
JailBreak Detect – Anti JailBreak Detect
沙盒完整性检测
iOS设备上,用户app安装在/var/mobile/Application中受沙盒限制,而系统app安装在/Application中不受沙盒限制。越狱设备上很多第三方app也安装在/Application下从而不受沙盒限制而拥有更多权限。一些越狱工具会移除沙盒限制以允许特定行为(如fork vfork popen)
int result = fork();
if(!result)
exit(0);
if(result >= 0)//jail broken
{sandbox_is_compromised = 1};
监测点2:在沙盒中,执行opendir(“/dev”)会返回NULL
监测点3:system() getgid() ??
文件系统检测
检测常见的越狱工具目录和文件是否存在
struct stat s;
int is_jailbroken = stat(“/Applications/Cydia.app”, &s) == 0;
常见的目录和文件
/Applications/MxTube.app
/Applications/blackra1n.app
/Applications/RockApp.app
/Applications/WinterBoard.app
/Applications/SBSettings.app
/Library/LaunchDaemons/com.openssh/sshd.plist
/Applications/IntelliScreen.app
/Library/MobileSubstrate/DynamicLibraries/Veency.plist
/Applications/FakeCarrier.app
/private/var/mobile/Library/SBSettings/Themes
/System/Library/LaunchDaemons/com.saurik.Cydia.Startup.plist
/Library/MobileSubstrate/DynamicLibraries/LiveClock.plist
/System/Library/LaunchDaemons/com.ikey.bbot.plist
/Applications/Icy.app
/Applications/Loader.app
/private/var/tmp/cydia.log
/Library/MobileSubstrate/MobileSubstrate.dylib
/private/var/stash
/private/var/lib/apt
/private/var/lib/cydia
/usr/libexec/cydia
/usr/libeec/sftp-server
/var/cache/apt
/var/lib/apt
/var/lib/cydia
/var/log/syslog
/var/tmp/cydia.log
/var/tmp/cydia.log
/bin/bash
/bin/sh
/usr/sbin/sshd
/bin/mv
/usr/libexec/ssh-keysign
/etc/ssh/sshd_config
/etc/apt
检测装载点
检测fstab
越狱工具会替换/etc/fstab文件导致变小,IOS5上正常为80字节
struct stat s;
stat(“/etc/fstab”, &s);
return s.st_size;
statfs函数检测
在非越狱机上statfs(“/”)应该返回如下标志:buf->f_flags = MNT_RDONLY + MNT_ROOTFS + MNT_DOVOLFS + MNT_JOURNALED + MNT_MULTILABEL,同时statfs(“/var/mobile/Container/Data/Application/<APP_GUID>”)应该返回如下标志:buf->f_flags = MNT_NOSUID + MNT_NODEV + MNT_DOVOLFS + MNT_JOURNALED + MNT_MULTILABEL
检测软链接
检测/Appliations软链接,越狱工具会将其替换到/var/stash/…下
struct stat s;
if(lstat(“/Applications”, &s) != 0)[
if(s.st_mode & S_IFLNK)
exit(-1);
}
其他软链接
/Library/Ringtones
/Library/WallPaper
/usr/arm-apple-darwin9
/usr/include
/usr/libexec
/usr/share
/var/stash/Library/Ringtones
/var/stash/usr/include
/var/stash/Library/WallPaper
/var/stash/usr/libexec
/var/stash/usr/share
/var/stash/usr/arm-apple-darwin9
URL Scheme检测
在越狱机上Cydia会创建一个cydia://的URL scheme,因此如果调用该Scheme返回成功则机器越狱
[NSURL URLWithString @”cydia://package/com.example.package”]
系统内核环境变量检测
越狱时会增加2个内核环境变量用于绕过iOS代码签名机制,sysctlbyname函数用于检测系统信息,在非越狱机上,下面值应该为1
sysctlbyname(security.mac.proc_enforce)
sysctlbyname(security.mac.vnode_enforce
检测DYLD_INSERT_LIBRARIES
检测DYLD_INSERT_LIBRARIES是否存在,越狱环境下会出现”/Library/MobileSubstrate/MobileSubstrate.dylib”,getenv(“DYLD_INSERT_LIBRARIES”) ,检测返回NULL和”\0”
运行进程检测
@try{
NSArray* processes = [self runningProcesses]
for(NSDictionary* dict in processes){
NSString* process = [dict objectForKey:@”ProcessName”];
if([process isEqualToString:@”MobileCydia”]){
return true;
}
else if([process isEqualToString:”Cydia”]){
return true
}
}
}
@catch(NSException* exception){
return 0
}
+ (NSArray*)runningProcesses{
int mib[4] = {CTL_KERN,KERN_PROC,KERN_PROC_ALL,0};
size_t miblen =4;
size_t size;
int st = sysctl(mib,miblen,NULL,&size,NULL,0);
struct kinfo_proc* process = NULL;
struct kinfo_proc* newprocess = NULL;
do{
size += size/10
newprocess = realloc(process,size);
if(!newprocess){
if(process){
free(process);
}
return nil;
}
int st = sysctl(mib,miblen,NULL,&size,NULL,0);
st = sysctl
}while(st == -1 && errno == ENOMEM);
}
if(st == 0){
if(size % sizeof(struct kinfo_proc) == 0){
int nprocess = size/sizeof(struct kinfo_proc);
if(nprocess){
NSMutableArray* array = [[NSMutableArray alloc] init];
for(int I = nprocess – 1;I >= 0;i--){
NSString* processID = [[NSString alloc] initWithFormat:@”%d”,process[i].kp_proc.p_pid];
NSString* processName = [[NSString alloc] initWithFormat:@”%d”,process[i].kp_proc.p_comm];
NSString* processPriority = [[NSString alloc] initWithFormat:@”%d”,process[i].kp_proc.p_priority];
NSDate* processStartDate = [NSDate dateWithTimeInternvalSince1970:process[i].kp_proc.p_un.__p_starttime.tv_sec];
NSDictionary* dict = [[NSDictionary alloc] initWithObjects:[NSArray arrayWithObjects:processID, processPriority, processName, processStartDate, nil] forKeys:[NSarray arrayWithObject:@”ProcessID”, @”ProcessPriority”, @”ProcessName”, @”ProcessStartDate”, nil]];
[array addObject:dict];
}
free(process);
return array;
}
}
return nil;
}
反检测方式:hook